|
Vocapedia >
USA > Gun violence >
Pro gun laws
Jeff Danziger
political cartoon
GoComics
November 01, 2022
https://www.gocomics.com/jeffdanziger/2022/11/01
Constitution for the United States of America
Second Amendment to the Constitution
Bill of Rights
Article the fourth [Amendment II] /
Second amendment
1789-1791
"A well regulated militia,
being necessary to the security of a free state,
the right of the people to keep and bear arms,
shall not be infringed"
http://memory.loc.gov/const/bor.html
http://memory.loc.gov/const/constquery.html
http://caselaw.lp.findlaw.com/data/constitution/amendment02/
http://www.archives.gov/exhibits/charters/bill_of_rights.html
The Constitution of the United States of
America > full text
pro-gun legislation
http://www.nytimes.com/2014/03/25/us/
amid-wave-of-pro-gun-legislation-georgia-proposes-sweeping-law.html
Missouri
http://www.nytimes.com/2016/09/16/
opinion/missouri-the-shoot-me-state.html
Florida
March 2018
https://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2018/03/05/
591036676/florida-senate-approves-gun-control-package-oks-arming-some-school-personnel
Texas
https://www.gocomics.com/jeffdanziger/2022/11/01
conceal
carry
https://www.gocomics.com/garyvarvel/2022/07/20
concealed
carry
https://www.nytimes.com/2022/11/03/
opinion/a-teacher-considers-arming-herself-in-the-classroom.html
Ohio's Kasich Signs
Gun Law Expanding Concealed Carry December 2016
http://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2016/12/21/
506481758/ohios-kasich-signs-new-gun-law-expanding-concealed-carry-in-daycares-colleges
Texans can now carry a handgun in public
without a permit or
the background check and training
the state previously
required. September 2021
Gun rights advocates
lauded the new state law
— called
"Constitutional Carry" by supporters —
for removing what
they considered an unfair burden
on gun owners.
https://www.npr.org/2021/09/02/
1033606817/texas-gun-law-permitless-carry-constitutional-carry
Texas >
'Campus-Carry'
concealed
carry law /
concealed weapons
allowed on Texas campuses
https://www.nytimes.com/2017/07/24/
opinion/why-i-bring-my-gun-to-school.html
http://www.nytimes.com/2016/08/28/us/
university-of-texas-campus-concealed-guns.html
http://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2016/08/01/
488262702/50-years-after-texas-college-shooting-campus-carry-becomes-law
http://www.npr.org/2016/07/31/
488122754/new-concealed-carry-law-on-texas-campuses-
coincides-with-grim-anniversary-of-aus
states allowing guns
on campus / so-called parling lot laws
http://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2016/12/21/
506481758/ohios-kasich-signs-new-gun-law-expanding-concealed-carry-in-daycares-colleges
http://www.nytimes.com/roomfordebate/2016/05/31/
should-guns-be-permitted-on-college-campuses
states allowing
employees to leave guns
in their cars in the
office parking lot.
http://www.npr.org/2014/12/12/
369833958/do-guns-on-the-premises-leave-workers-more-safe-or-less
gun laws
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/09/06/
opinion/school-shooting-georgia-dad-arrested.html
https://www.npr.org/2022/05/25/
1101139624/texas-elementary-school-shooting-sandy-hook-gun-legislation-gun-control
https://www.npr.org/2019/10/20/
771278167/poll-number-of-americans-who-favor-stricter-gun-laws-continues-to-grow
http://www.npr.org/2017/10/03/
555425837/las-vegas-massacre-prompts-further-look-into-nevadas-gun-laws
http://www.npr.org/2013/04/04/
176267948/states-head-in-different-directions-on-gun-legislation
http://www.nytimes.com/2012/12/19/
opinion/the-yawning-loophole-in-the-gun-laws.html
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/01/23/
opinion/23sun1.html
http://www.nytimes.com/2010/12/30/us/
30ohio.html
stricter gun laws
https://www.npr.org/2019/10/20/
771278167/poll-number-of-americans-who-favor-stricter-gun-laws-continues-to-grow
NRA-backed gun laws
http://www.npr.org/2017/10/05/
555859571/nra-backed-gun-laws-have-found-success-in-state-legislatures-across-the-u-s
Colorado gun laws
http://www.nytimes.com/2012/07/21/us/
colorado-gun-laws-remain-lax-despite-changes-after-columbine.html
Georgia gun laws
http://www.npr.org/2014/06/22/
324006448/georgias-new-pro-gun-law-triggers-confusion-for-some-residents
http://www.npr.org/blogs/thetwo-way/2014/04/23/
306228730/georgia-law-oks-guns-in-schools-churches
Nevada's gun laws
http://www.npr.org/2017/10/03/
555425837/las-vegas-massacre-prompts-further-look-into-nevadas-gun-laws
New York gun law / legislation
http://www.nytimes.com/2013/01/16/
opinion/new-york-leads-on-gun-control.html
http://www.nytimes.com/2013/01/16/nyregion/
tougher-gun-law-in-new-york.html
http://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2013/01/15/
nyregion/20130115nygun-document.html
Oregon gun laws
http://www.nytimes.com/2014/06/11/us/
troutdale-oregon-reynolds-high-school-shooting.html
Tennessee gun laws
https://www.npr.org/2018/04/23/
605103200/waffle-house-shooting-underscores-how-gun-laws-vary-from-state-to-state
Utah
concealed-carry
permit
https://www.nytimes.com/2022/11/03/
opinion/a-teacher-considers-arming-herself-in-the-classroom.html
Utah’s gun permit
http://www.nytimes.com/2010/07/06/us/
06guns.html
In
North Dakota,
No Need For A Permit
To Carry A Concealed Handgun
2017
http://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2017/03/24/
521368996/in-north-dakota-no-need-for-a-permit-to-carry-a-concealed-handgun
stand your ground
https://www.npr.org/2019/08/23/
753929898/florida-man-found-guilty-of-manslaughter-despite-stand-your-ground-defense
https://www.npr.org/2019/08/19/
752365033/stand-your-ground-trial-begins-in-florida-a-year-after-unarmed-black-man-is-kill
stand your ground law
> Florida
https://www.npr.org/2019/08/23/
753929898/florida-man-found-guilty-of-manslaughter-despite-stand-your-ground-defense
https://www.nytimes.com/2018/07/21/
us/florida-stand-your-ground.html
enact a Stand Your
Ground gun law
http://www.nytimes.com/2013/11/24/
opinion/sunday/more-stand-your-ground-fantasizing.html
gun shop
http://www.nytimes.com/2013/01/30/us/
strict-chicago-gun-laws-cant-stem-fatal-shots.html
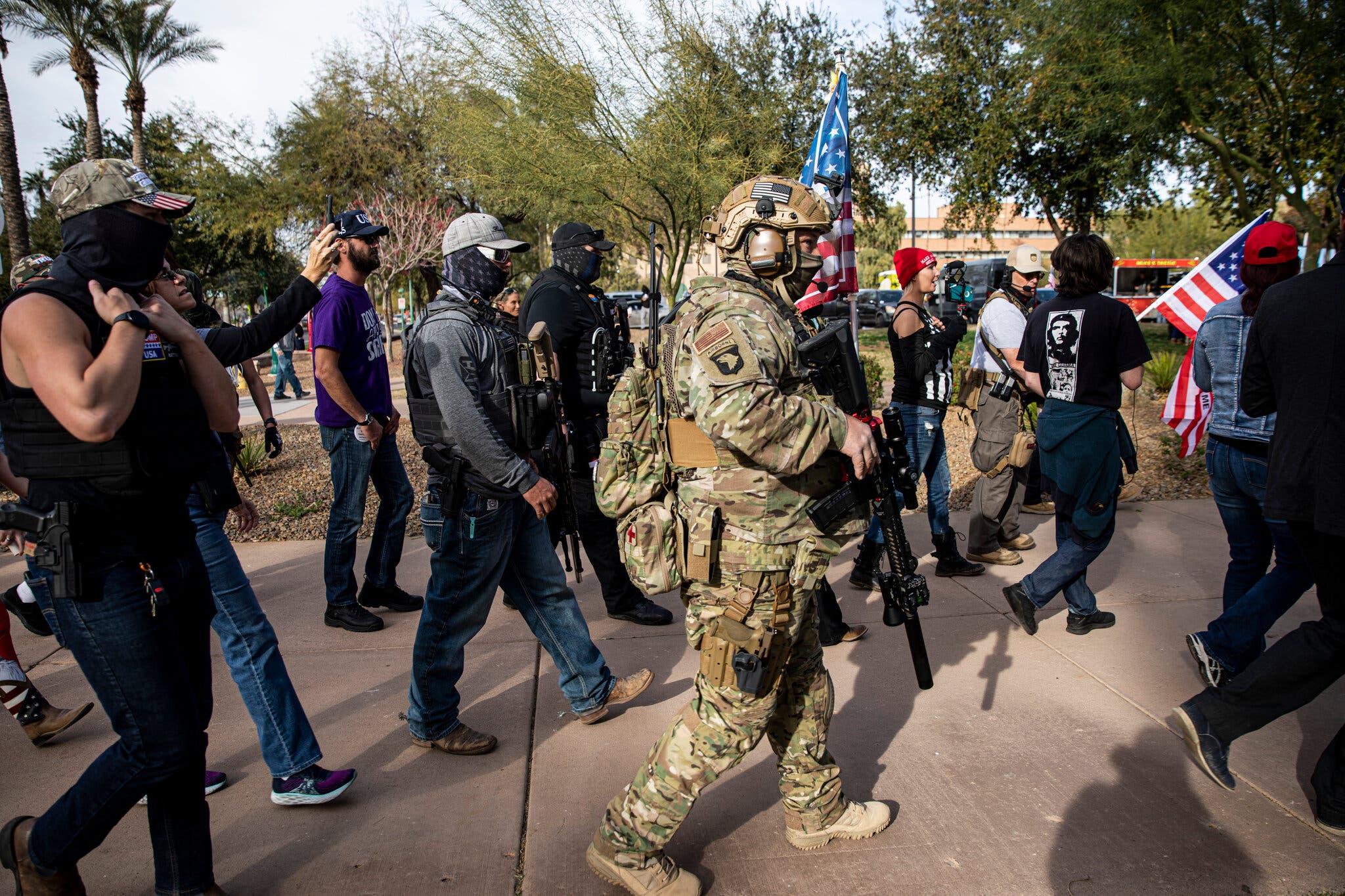

Armed protesters
at the Arizona
State Capitol in Phoenix on Jan. 6, 2021.
Photograph:
Adriana Zehbrauskas
for The New York
Times
At Protests, Guns
Are Doing the Talking
Armed Americans,
often pushing a right-wing agenda,
are increasingly
using open-carry laws
to intimidate
opponents and shut down debate.
NYT
Nov. 26, 2022
Updated 9:59 a.m. ET
https://www.nytimes.com/2022/11/26/
us/guns-protests-open-carry.html
open carry
https://www.nytimes.com/2022/11/26/
us/guns-protests-open-carry.html
USA > open carry of
handguns in Texas UK
http://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2016/jan/01/
texas-open-carry-handguns-law-public-places-businesses
gun culture > South Dakota
March 2013
a state with deep roots in hunting,
where children start learning
how to shoot BB guns when they are 8,
skeet shoot with shotguns by age 14
and enter target shooting contests
with .22-caliber semiautomatic rifles.
http://www.nytimes.com/2013/03/09/us/
south-dakota-gun-law-classrooms.html
Corpus of news articles
USA > Gun
violence > Laws >
Gun rights, Pro
gun laws / legislation
Shop
Owners Report
Rise in Firearm Sales
as
Buyers Fear
Possible New Laws
December
21, 2012
The New York Times
By STEPHANIE CLIFFORD
Rainier
Arms, a gun dealer in Auburn, Wash., receives great Yelp reviews for its
responsiveness. But a call to the dealer on Friday led to a full voice mail box,
and an e-mail to its sales team drew this automatic response: “Thank you for
contacting Rainier Arms for your AR-15 needs. Due to an overwhelming response to
the latest political climate, we are experiencing longer-than-normal response
times.”
At Bud’s Gun Shop in Maryland, a message on the Web site said that customer
service was “completely overwhelmed” and it discouraged customers from calling
or e-mailing.
And on GunBroker.com, an Oracle .223 that normally retails for around $650 had
been bid up to $1,175 with three days left in the auction.
With gun-control legislation getting more serious discussion than it has in
years, gun sales are spiking as enthusiasts stock up in advance of possible
restrictions.
Gun sales have been increasing over the past five years, with marked increases
around the 2008 and 2012 elections, and after mass shootings like the one in
Aurora, Colo., and now in Newtown, Conn.
“The largest factor by far is fears over a potential change in gun laws — that’s
what’s driving most guns enthusiasts or even first-time buyers to go buy a gun,”
said Nima Samadi, senior guns and ammunition analyst for the research firm
IBISWorld.
There is increasing demands for guns in the United States. Last year, the
Federal Bureau of Investigation conducted 16.45 million background checks for
firearm sales through the National Instant Criminal Background Check System, a
14 percent jump from the previous year. In the first 11 months of this year, the
bureau conducted 16.8 million background checks, a record since the system’s
founding in 1998.
Since the shootings at Sandy Hook Elementary School in Newtown, though, a few
companies associated with gun sales have backed away. Cerberus Capital
Management put the company that makes the Bushmaster, a gun used in the
shootings, up for sale on Tuesday, saying, “The Sandy Hook tragedy was a
watershed event that has raised the national debate on gun control to an
unprecedented level.”
Dick’s Sporting Goods temporarily ceased selling all guns in its location
closest to Newtown, and has also put a hold on sales of so-called modern
sporting rifles, which include semiautomatic guns, nationwide.
And Deseret Digital Media, which owns KSL.com, a Web site that has been
criticized by Mayor Michael R. Bloomberg for allowing unregulated gun sales,
said it was suspending classified advertisements for guns.
Elsewhere, though, consumers are hurrying to buy guns, leading to some models
being out of stock, warnings of shipping and customer-service delays, and
significant premiums on assault rifles.
“We are seeing a total madhouse of buying everything in sight,” said Bob Irwin,
owner of the Gun Store, a Las Vegas shooting range and retailer. Thursday, he
said, was the largest sales day in the history of the store, which has been open
for 30 years. “We have not only a run on the guns, but a run on ammunition.”
Mr. Irwin has begun limiting how much of some types of ammunition customers can
buy, and he has canceled employees’ days off to handle the demand.
Walmart, the largest retailer of guns and ammunition in the United States,
indicated that several semiautomatic guns were out of stock at locations across
the country. Kory Lundberg, a spokesman, said the company was not sold out of
guns altogether, but had low inventory in some situations. Walmart carries guns
in about half its stores, and about one-third carry so-called modern sporting
rifles, the category including the Bushmaster and other AR-15 weapons.
Other retailers around the country were selling out of guns and accessories. On
Friday on ImpactGuns.com, the Bushmaster .223 was out of stock. Davidson’s, a
supplier to gun retailers, placed a notice on its Web site that said it was
seeing “unprecedented demand,” and at MidwayUSA.com, more than 100 parts for
AR-15 guns were out of stock and on back order.
On AR15.com, a gun-enthusiast Web site, a user posted that a barrel for a gun
disappeared from an online shopping cart overnight, and is now on back order.
Another user, named warplg8654, responded, “Dealers can’t keep anything in stock
for what I think are obvious reasons given the current political climate.”
When a user called JazzFan asked whether paying a $100 premium for a Stag Model
3 was a good deal, another user said that seemed “reasonable with all of the
panic buying.”
Gavin Gear, the founder of the enthusiast site Northwest Gun, said gun owners
were feeling “apprehension.”
“People are trying to think ahead, and if they want to own a particular firearm
and they think it’s going to be outlawed or restricted, they’re more likely to
buy now,” he said.
Shop Owners Report Rise in Firearm Sales
as Buyers Fear Possible New Laws,
NYT,
21.12.2012,
https://www.nytimes.com/2012/12/22/
nyregion/gun-shop-owners-report-spike-in-sales-
as-enthusiasts-fear-possible-new-laws.html
Personal
Guns
and the Second Amendment
December
17, 2012
The New York Times
When the
Supreme Court struck down a ban on handguns by the District of Columbia in 2008,
ruling that there is a constitutional right to keep a loaded handgun at home for
self-defense, the decision was enormously controversial in the legal world. But
the court’s conclusion has generally been accepted in the real world because the
ruling was in tune with popular opinion — favoring Americans’ rights to own guns
but also control of gun ownership.
The text of the Second Amendment creates no right to private possession of guns,
but Justice Antonin Scalia found one in legal history for himself and the other
four conservatives. He said the right is not outmoded even “in a society where
our standing army is the pride of our Nation, where well-trained police forces
provide personal security, and where gun violence is a serious problem.”
It is not just liberals who have lambasted the ruling, but some prominent
conservatives like Judge J. Harvie Wilkinson III of the United States Court of
Appeals for the Fourth Circuit. The majority, he wrote, “read an ambiguous
constitutional provision as creating a substantive right that the Court had
never acknowledged in the more than two hundred years since the amendment’s
enactment. The majority then used that same right to strike down a law passed by
elected officials acting, rightly or wrongly, to preserve the safety of the
citizenry.” He said the court undermined “conservative jurisprudence.”
In the real world, however, criticism has abated in part because the majority
opinion was strikingly respectful of commonplace gun regulations. “Like most
rights,” Justice Scalia said, “the right secured by the Second Amendment is not
unlimited.”
And: “nothing in our opinion should be taken to cast doubt on longstanding
prohibitions on the possession of firearms by felons and the mentally ill, or
laws forbidding the carrying of firearms in sensitive places such as schools and
government buildings, or laws imposing conditions and qualifications on the
commercial sale of arms. We also recognize another important limitation on the
right to keep and carry arms” —“prohibiting the carrying of ‘dangerous and
unusual weapons.’ ”
Justice Scalia does not say how federal courts should evaluate such regulations
and the Supreme Court may need to return to this issue soon, to resolve a
substantial disagreement that has arisen in federal appeals courts.
Does the court’s 4-year-old ruling imply “a right to carry a loaded gun outside
the home”? That is what the Seventh Circuit appellate court concluded last week
in striking down an Illinois law that prohibited most people from carrying a
loaded weapon in public.
Or does the Supreme Court’s ruling on handguns support the view that public
interest in safety outweighs an individual’s interest in self-defense because
gun rights are more limited outside the home? That is what the Second Circuit
found last month in upholding a New York State law limiting handgun possession
in public to people who can show a threat to their own safety.
Where “gun violence is a serious problem,” as Justice Scalia said it is in the
United States, the courts must be very cautious about extending the individual
right to own a gun. The justice’s opinion made that clear.
Read related editorials on gun control:
rethinking guns and legislation
abroad.
Personal Guns and the Second Amendment,
NYT, 17.12.2012,
http://www.nytimes.com/2012/12/18/
opinion/the-gun-challenge-second-amendment.html
The
Great Gun Gag
December 6,
2012
9:00 pm
The New York Times
By TIMOTHY EGAN
On national
television, you can talk about the sordid details of your sex life, the depth of
your religious piety or your belief that an organization that no longer exists,
Acorn, stole the 2012 presidential election -- a fantasy held by half of
Republicans. You can call climate change a hoax, you can say the moon landing
never happened, you can even praise Alex Rodriguez, though you shouldn't.
But you cannot talk about the 300 million or more guns circulating in private
hands in the United States. The most armed society in the world, ranked first
among 179 nations in the rate of gun ownership, had 9,146 gun homicides in 2009.
The same year, Canada had 173. But don't bring that up.
In Florida, it was against the law -- until the law was blocked by a federal
judge last summer -- for hospital doctors to even ask about firearms ownership
of victims, even though gunshot wounds account for 1 in 25 emergency room
visits.
Conservatives complain about anti-free-speech vigilantes who keep incendiary
voices of the right from being heard on college campuses, and they have a valid
point. But some of these same First Amendment defenders are the first to smother
any talk about the American weapons culture. The gun gag rules.
The latest public figure to face the shame shower is Bob Costas, the sports
broadcaster who occasionally steps outside the chalk lines of the games he
covers. Last Sunday, a day in late autumn devoted as usual to the lucrative
violence of professional football, Costas spoke about a more tragic kind of
violence. In passing on the words of a local writer, he wondered whether the
Kansas City Chiefs linebacker Jovan Belcher and his girlfriend might still be
alive had guns not been so readily available. Belcher, who kept a handgun on the
kitchen table and an assault rifle in the den, shot Kasandra Perkins, the mother
of their infant child, and then himself last weekend.
Costas made his brief remarks at halftime of the Sunday night game. Within
minutes, the censors went after him. Top Republicans called for his resignation.
Rush Limbaugh and Michelle Malkin, who are to reasoned argument what salt is to
a slug, condemned him. And Herman Cain, the pizza guy who at one point led the
Republican presidential primary field in the polls, passed on this tweet:
"Excuse me, Bob Costas, but you are an idiot, so shut up."
Those last two words pretty much define the current climate regarding debate
about guns and violence. In this country, it is the issue that dare not speak
its name.
Costas said later he had nothing against the Second Amendment. But our gun
culture more often than not leads to tragedy, he noted. In this, he was stating
a fact, not an opinion. "Give me one example of an athlete -- and I know it's
happened in society -- but give me one example of a professional athlete who by
virtue of having a gun took a dangerous situation and turned it around for the
better," he said.
My sentiments are with Costas. I've lost friends and family members to gun
violence. Still, I have nothing against people exercising their Second Amendment
rights. Adults can have all the guns they want, but please -- they should
understand that their arsenal makes them less safe.
People with guns in the home are at a far greater risk of dying of homicide than
those without, the American Journal of Epidemiology reported in 2004. For men,
the likelihood of death by suicide is much higher if a gun is nearby. And 90
percent of suicide attempts by gun are successful; for willful drug overdoses,
the rate is only 2 percent.
Understandably, people buy guns for self-defense. But a gun in the home is 12
times more likely to result in the death of a household member, or a visitor,
than an intruder, a 2010 study by the official journal of the Southern Medical
Association found.
For all those grim numbers, the United States is not the most violent society.
Drug oligarchies and broken tribal nations are much more lethal places to live.
But among the 23 wealthiest countries, the United States is easily the
bloodiest: homicide gun rates are 19.5 times higher here than in any other
high-income country, Politifact reported.
Going into a theater or a mall in America can be a risky thing, as recent mass
shootings have shown. I just returned from Idaho, where people are buying guns
at a record clip because of the delusional fear that President Obama is going to
take them away. The safest place in Idaho, by far, is just inside the security
line at the Boise airport, where a big sign warns people that they will soon be
entering a mandatory gun-free zone.
How these basic truths came to be treated as unmentionables is a tribute to the
gun lobby's power to strangle debate on even simple safety questions. At the
same time, they have all but shut down public health research into gun violence.
For the politicians and pundits who do the gun industry's bidding, the First
Amendment does not apply to the Second Amendment. It took a sportscaster,
accustomed to parsing the nuances of a stunt blitz, to break the code of
shameful silence.
The Great Gun Gag, NYT, 6.12.2012,
http://opinionator.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/12/06/the-great-gun-gag/
The Human Cost
of the Second Amendment
September 26, 2012
8:30 pm
The New York Times
Opinionator
A Gathering of Opinion From Around the Web
By THERESA BROWN
Wisconsin, Aurora, Virginia Tech, Columbine. We all know these
place names and what happened there. By the time this column appears, there may
well be a new locale to add to the list. Such is the state of enabled and
murderous mayhem in the United States.
With the hope of presenting the issue of guns in America in a novel way, I'm
going to look at it from an unusual vantage point: the eyes of a nurse. By that
I mean looking at guns in America in terms of the suffering they cause, because
to really understand the human cost of guns in the United States we need to
focus on gun-related pain and death.
Every day 80 Americans die from gunshots and an additional 120 are wounded,
according to a 2006 article in The Journal of Policy Analysis and Management.
Those 80 Americans left their homes in the morning and went to work, or to
school, or to a movie, or for a walk in their own neighborhood, and never
returned. Whether they were dead on arrival or died later on in the hospital, 80
people's normal day ended on a slab in the morgue, and there's nothing any of us
can do to get those people back.
In a way that few others do, I became aware early on that nurses deal with death
on a daily basis. The first unretouched dead bodies I ever saw were the two
cadavers we studied in anatomy lab. One man, one woman, both donated their
bodies for dissection, and I learned amazing things from them: the sponginess of
lung tissue, the surprising lightness of a human heart, the fabulous intricacy
of veins, arteries, tendons and nerves that keep all of us moving and alive.
I also learned something I thought I already knew: death is scary. I expected my
focus in the lab to be on acquiring knowledge, and it was, but my feelings about
these cadavers intruded also. I had nightmares. The sound of bones being sawed
and snapped was excruciating the day our teaching assistant broke the ribs of
one of them to extract a heart. Some days the smell was so overwhelming I wanted
to run from the lab. Death is the only part of life that is really final, and I
learned about the awesomeness of finality during my 12 weeks with those two very
dead people.
Of course, in hospitals, death and suffering are what nurses and doctors
struggle against. Our job is to restore people to health and wholeness, or at
the very least, to keep them alive. That's an obvious aim on the oncology floor
where I work, but nowhere is the medical goal of maintaining life more
immediately urgent than in trauma centers and intensive-care units. In those
wards, patients often arrive teetering on the border between life and death, and
the medical teams that receive them have fleeting moments in which to act.
The focus on preserving life and alleviating suffering, so evident in the
hospital, contrasts strikingly with its stubborn disregard when applied to lives
ended by Americans lawfully armed as if going into combat. The deaths from guns
are as disturbing, and as final, as the cadavers I studied in anatomy lab, but
the talk we hear from the gun lobby is about freedom and rights, not life and
death.
Gun advocates say that guns don't kill people, people kill people. The truth,
though, is that people with guns kill people, often very efficiently, as we saw
so clearly and so often this summer. And while there can be no argument that the
right to bear arms is written into the Constitution, we cannot keep pretending
that this right is somehow without limit, even as we place reasonable limits on
arguably more valuable rights like the freedom of speech and due process.
No one argues that it should be legal to shout "fire" in a crowded theater; we
accept this limit on our right to speak freely because of its obvious real-world
consequences. Likewise, we need to stop talking about gun rights in America as
if they have no wrenching real-world effects when every day 80 Americans, their
friends, families and loved ones, learn they obviously and tragically do.
Many victims never stand a chance against a dangerously armed assailant, and
there's scant evidence that being armed themselves would help. Those bodies skip
the hospital and go straight to the morgue. The lucky ones, the survivors - the
120 wounded per day - get hustled to trauma centers and then intensive care
units to, if possible, be healed. Many of them never fully recover.
A trauma nurse I know told me she always looked at people's shoes when they lay
on gurneys in the emergency department. It struck her that life had still been
normal when that patient put them on in the morning. Whether they laced up
Nikes, pulled on snow boots or slid feet into stiletto heels, the shoes became a
relic of the ordinariness of the patient's life, before it turned savage.
So I have a request for proponents of unlimited access to guns. Spend some time
in a trauma center and see the victims of gun violence - the lucky survivors -
as they come in bloody and terrified. Understand that our country's blind
embrace of gun rights made this violent tableau possible, and that it's playing
out each day in hospitals and morgues all over the country.
Before leaving, make sure to look at the patients' shoes. Remember that at the
start of the day, before being attacked by a person with a gun, that patient
lying on a stretcher writhing helplessly in pain was still whole.
Theresa Brown is an oncology nurse and the author of
"Critical Care: A New Nurse Faces Death, Life,
and Everything in
Between."
The Human Cost of the Second Amendment,
NYT, 26.9.2012,
http://opinionator.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/09/26/
the-human-cost-of-the-second-amendment/
6,000
Bullets
July 23,
2012
The New York Times
With the
ease of downloading a song, anyone with a computer and a credit card can order
thousands of bullets and shotgun shells on the Internet, along with tear-gas
canisters and speed loaders. They can get the same high-capacity ammunition
clips that infantry soldiers use. They can even get bulletproof vests and SWAT
helmets. All without fear of a single background check.
No one is paying attention to whether buyers have criminal histories or
mental-health records. No one is monitoring bulk sales of ammunition to see who
might be building an arsenal. Even after a young man in Colorado buys 6,000
rounds by mail order and uses them to commit mass murder, it is the rare
politician who proposes to make the tools of terror slightly harder to obtain.
When he was campaigning for office in 2008, Barack Obama vowed to reinstate the
assault weapons ban that had expired in 2004. That would have prohibited the
AR-15 rifle used in the Colorado theater shooting on Friday, along with the
large 100-round magazine attached to it. But as president, Mr. Obama has made no
attempt to do so. Mitt Romney banned assault weapons as governor of
Massachusetts and undoubtedly saved many lives, but now he opposes all gun
control measures. He never repeats what he said in 2004 when he signed the ban:
“Deadly assault weapons have no place in Massachusetts,” he said. “They are
instruments of destruction with the sole purpose of hunting down and killing
people.”
Both men fear the power of gun ideologues, particularly in swing states like
Pennsylvania, Nevada and North Carolina, where many voters have fallen under the
spell of a gun lobby that considers any restriction an unthinkable assault on
the Constitution. Senator Ron Johnson, the Tea Party favorite from Wisconsin,
spoke for the Republican Party (and many Democrats) when he said that limiting
high-capacity magazines would infringe on a basic right. “When you try and do
it, you restrict our freedom,” he said on “Fox News Sunday.”
Freedom to do what, precisely? To fire off 100 rounds without reloading? A few
sport shooters may enjoy doing that on a firing range, but that’s hardly
sufficient reason to empower someone else to do it in a movie theater. It has
nothing to do with the basic right of home protection and self-defense found by
the Supreme Court in 2008.
A Democratic senator, Frank Lautenberg of New Jersey, is one of the few
officials courageous enough to propose a better idea: A ban on clips that hold
more than 10 bullets, which are not needed to hunt, practice or protect oneself.
He first proposed this last year, after a gunman in Tucson used a 33-round
magazine to shoot 18 people, including Representative Gabrielle Giffords,
killing six. The shooter was tackled when he had to reload.
The ban went nowhere and will undoubtedly be laughed off by gun advocates this
year, too. In 1993, they killed a proposal by Senator Daniel Patrick Moynihan of
New York to impose a heavy tax on handgun ammunition, especially the bullets
that expand and cause heavy tissue damage. A few years ago, Gov. Arnold
Schwarzenegger of California signed a law requiring identification to buy
handgun ammunition and forbidding mail-order sales. A group of gun sellers sued
and won a trial-court ruling that the law was too vague. (The state attorney
general, Kamala Harris, appealed the ruling in February.)
But the gun lobby’s legal and political victories can’t obscure the facts. The
assault weapons ban didn’t clearly reduce crime, the best study of the measure
found, but allowing high-capacity magazines would “result in more shots fired,
more persons hit, and more wounds inflicted per victim than do attacks with
other firearms.” Sensible restrictions on ammunition and clips won’t eliminate
mass shootings; they may make them less likely and reduce their level of
violence.
Many politicians of both parties know this. To overcome their fear of the gun
lobby, they need only look at the faces of the victims in Aurora, Colo.
6,000 Bullets, NYT, 23.7.2012,
http://www.nytimes.com/2012/07/24/
opinion/6000-bullets-in-colorado.html
Silencing the Guns
March 26,
2012
11:55 pm
The New York Times
By DREW WESTEN
When
Gabrielle Giffords tendered her resignation from the House of Representatives to
Speaker John Boehner because she did not feel she could continue to serve at her
current level of disability, the entire House erupted in a rare moment of
bipartisan unity, supporting their brave colleague who had survived a bullet
through the brain at point-blank range.
That was not, however, the first bipartisan moment related to the attack on
Gabby Giffords, nor would it be the last. In 2004, Congress let the assault
weapons ban Bill Clinton had passed “sunset” despite overwhelming public
support. That law limited the number of rounds of ammunition a shooter could
fire before having to reload, and letting it die an untimely death allowed a
mentally ill young man in Tucson to purchase a handgun with a 33-round magazine.
Had the assault weapons ban remained in place, he may well have been able to
shoot the congresswoman, but he would not have been able to empty his clip,
killing 6 people and wounding 13 others, before being tackled to the ground.
That moment was followed by another bipartisan moment, when President Obama
delivered a moving speech on Jan. 12 at the scene of the carnage in Tucson. In
it, the president called on the nation to mourn not only the shooting of a
beloved member of Congress but the lives of the people who died at the hands of
Giffords’ assailant, including a 9-year-old girl and a federal judge. But on
neither that national day of mourning nor on any day since has the president or
the members of Congress, who are either too frightened or too corrupted by the
National Rifle Association, honored Giffords or the memory of those who died in
that massacre in Tucson in the most appropriate way: with a return to common
sense, like reestablishing the assault weapons ban that might have saved their
lives. Later in January, Representative Carolyn McCarthy and Senator Frank
Lautenberg proposed legislation to outlaw high-capacity magazines; it has gone
nowhere.
The first President Bush, unlike his swaggering son (who advocated the demise of
a ban on assault weapons whose sole purpose is to hunt humans) showed political
courage by publicly quitting the N.R.A. in disgust in 1995 when it began
advocating ideas like its contention that citizens need military-style assault
weapons to protect themselves against our own government (members, for example,
of the National Guard). In colorful but paranoid language, it called law
enforcement officers “jack-booted government thugs,” prompting the elder Bush to
condemn the group for its disrespect for the law and those who defend it. Since
then, it has successfully advocated for increasingly radical laws. One of them,
of course, is Florida’s “stand your ground” law, which discourages de-escalation
of potential firefights in public with predictable results, like the shooting
death in Sanford, Fla., of Trayvon Martin.
Between the Giffords massacre and Martin’s death, we have seen more shootings
and more bipartisan moments. Around the anniversary of the Tucson massacre that
cut short the congressional career of an extraordinary woman — a woman I had
come to know personally and adore in her five years in Congress — came two more
mass killings. One occurred in Chardon High School in a small town in Ohio, as a
17-year-old opened fire on students with a Ruger .22-caliber semiautomatic with
a capacity of 10 rounds. Fortunately the alleged shooter, T.J. Lane, didn’t have
access to a gun with more firepower. About two weeks later, a man entered one of
the nation’s premiere medical centers, at the University of Pittsburgh, with two
semiautomatic handguns, and opened fire.
And in yet another show of bipartisanship, political leaders on both sides of
the aisle put on their silencers. If an assassination attempt on one of their
own did not move members of Congress to ask whether the N.R.A. has a little too
much sway in their chambers, a few dead and wounded teenagers, medical patients,
and their family members were not going to unlock their safeties. Most have
clearly made the risk assessment that they have more to fear from the N.R.A.
than they do from an occasional sniper. In the 2010 election cycle, the N.R.A.
spent over $7 million in independent expenditure campaigns for and against
specific candidates, and it has a remarkable record of success at taking out
candidates and elected officials with the misfortune of being caught in its
crosshairs.
Over a million Americans have lost their lives to gunfire since that awful
spring of 1968 when both Bobby Kennedy and Martin Luther King, Jr. were killed
by assassins’ bullets. Last year alone guns killed or wounded another 100,000
Americans; roughly 30,000 of them died. Had that occurred elsewhere, we
would call it genocide. We don’t know exactly how many have been killed in the
fighting in Libya, Egypt and Syria, but our elected officials have had far less
trouble calling for the ouster of Middle Eastern leaders than the leadership of
the N.R.A. But it’s not just money that prevents common-sense action on gun
violence in America. Millions of Americans hunt, and a third of all households
in the United States own a gun. Guns were part of the frontier culture that
shaped the American psyche, and hunting has passed from generation to generation
in much of America. As a son of the South, I could give an intruder a run for
his money (although, like most people, I would do better to rely first on our
security service and the loud alarm a break-in sets off), and I put on my
thickest Southern accent and tease my soon-to-be teenage daughter that I’ll be
out on the front porch “cleaning my shotgun” when her first date arrives at the
door.
In so many cases, it’s a failure of our leaders — Republicans, who prey on the
fears of their constituents and don’t even bother anymore to hide the puppet
strings pulled by large corporations, and Democrats, who too frequently forget
that humans are supposed to be vertebrates (and hence to have a spine) — to
speak to Americans’ ambivalence about guns. Over the years in my capacity as a
strategic messaging consultant, I’ve tested a range of messages on guns, and the
messages that resonate with hunters and gun owners sound like this: “If you need
an M-16 to hunt deer, you shouldn’t be anywhere near a damned gun,” or “If
you’re hunting with an AK-47, you’re not bringing that meat home for dinner.”
The first things responsible hunters teach are never to point a gun anywhere but
up or down unless you mean to shoot, and where the safety is.
It’s no wonder that Democrats have backed off of even talking about guns since
Clinton signed the Brady Bill and the assault weapons ban into law nearly two
decades ago. The last thing you want to be armed with as an advocate of common
sense are phrases like “gun control,” which makes a government-wary public and
law-abiding gun-owners uneasy — and susceptible to tendentious “slippery slope”
arguments about how “they want to take away your guns.” In contrast, everyone
but the lunatic fringe in America supports gun safety laws — such as eliminating
the gun-show loophole that allows the sale of military-grade weapons without
background checks, and has led to the deaths of tens of thousands of Americans
as well as Mexicans, whose drug cartels find the loophole extremely helpful.
Democrats could steel their spines if they could find the point of intersection
between law-abiding gun owners and law-abiding citizens who may or may not own a
gun but want to keep their families safe. In national testing, we’ve found that
a simple, non-equivocating statement focusing on that point of intersection —
law-abiding — beats the toughest “they want to take away your guns” message we
can fire at it. It leads every demographic group other than those who stockpile
weapons to support common-sense gun safety laws. Offered a message that speaks
to their ambivalence, people readily recognize that a 33-round clip makes it
virtually impossible to tackle a shooter until he has had time to kill 15 or 16
people. They understand that allowing people to purchase military-style weapons
at gun shows without a background check renders gun safety laws meaningless. And
they find it incomprehensible that we have laws on the books that tie the hands
of law enforcement officials trying to track down where a gun was bought and
sold, and that we keep such sloppy records that criminals, people with a history
of commitment for care for serious mental illness, and people with active
restraining orders on them can slip by background checks even where they’re
required.
Beginning with a statement of principle both makes clear the speaker’s intent
and inoculates against all the slippery-slope arguments used by the N.R.A. and
the elected officials in its employ or fearful of its power: “My view on guns
reflects one simple principle: that our gun laws should guarantee the rights and
freedoms of all law-abiding Americans. That’s why I stand with the majority who
believe in the right of law-abiding citizens to own guns to hunt or protect
their families. And that’s why I stand with the majority who believe they have
the right to send their kids to school and see them return home safely at
night.” Versions of a message containing that principle win by over a 2:1 margin
with independents, and they win in every region of the country, including in my
own backyard, in the red clay of Georgia.
This shouldn’t be an issue of left or right. Grocery stores in Tucson, where
Gabby Giffords was shot (and where my mother-in-law shops — she just happened to
be out of town that Saturday), are not hotbeds of “socialism.” I don’t know the
party affiliations of the fallen teenagers in Chardon or the staff members,
patients or families in Pittsburgh, but I suspect they ranged across the
political spectrum.
Guns don’t kill people. Silence does.
Drew Westen is
a professor of psychology
at Emory University
and the author
of “The Political Brain:
The Role of
Emotion
in Deciding the Fate of the Nation.”
Silencing the Guns,
NYT, 26.3.2012,
http://campaignstops.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/03/26/
silencing-the-guns/
How Many Deaths Are Enough?
January 17, 2011
The New York Times
By BOB HERBERT
On April 22, 2008, almost exactly one year after 32 students and faculty
members were slain in the massacre at Virginia Tech, the dealer who had sold one
of the weapons used by the gunman delivered a public lecture on the school’s
campus. His point: that people at Virginia Tech should be allowed to carry
concealed weapons on campus.
Eric Thompson, owner of the online firearms store that sold a .22-caliber
semiautomatic handgun to the shooter, Seung-Hui Cho, did not think that his
appearance at Virginia Tech was disrespectful or that his position was extreme.
He felt so strongly that college students should be allowed to be armed while
engaged in their campus activities that he offered discounts to any students who
wanted to buy guns from him.
Thompson spun the discounts as altruistic. He told ABCNews.com, “This offers
students and people who might not have otherwise been able to afford a weapon to
purchase one at a hefty discount and at a significant expense to myself.”
The sale to Cho was not Thompson’s only unfortunate link to a mass killer. His
firm sold a pair of 9-millimeter Glock magazines and a holster to Steven
Kazmierczak, a 27-year-old graduate student in DeKalb, Ill., who, on the
afternoon of Feb. 14, 2008, went heavily armed into an auditorium-type lecture
hall at Northern Illinois University. Kazmierczak walked onto the stage in front
of a crowd of students and opened fire. He killed five people and wounded 18
others before killing himself.
We’ve allowed the extremists to carry the day when it comes to guns in the
United States, and it’s the dead and the wounded and their families who have had
to pay the awful price. The idea of having large numbers of college students
packing heat in their classrooms and at their parties and sporting events, or at
the local pub or frat house or gymnasium, or wherever, is too stupid for words.
Thompson did not get a warm welcome at Virginia Tech. A spokesman for the
school, Larry Hincker, said the fact that he “would set foot on this campus” was
“terribly offensive” and “incredibly insensitive to the families of the
victims.”
Just last week, a sophomore at Florida State University, Ashley Cowie, was shot
to death accidentally by a 20-year-old student who, according to authorities,
was showing off his rifle to a group of friends in an off-campus apartment
complex favored by fraternity members. A second student was shot in the wrist.
This occurred as state legislators in Florida are considering a proposal to
allow people with permits to carry concealed weapons on campuses. The National
Rifle Association thinks that’s a dandy idea.
The slaughter of college students — or anyone else — has never served as a
deterrent to the gun fetishists. They want guns on campuses, in bars and taverns
and churches, in parks and in the workplace, in cars and in the home. Ammunition
everywhere — the deadlier, the better. A couple of years ago, a state legislator
in Arizona, Karen Johnson, argued that adults needed to be able to carry guns in
all schools, from elementary on up. “I feel like our kindergartners are sitting
there like sitting ducks,” she said.
Can we get a grip?
The contention of those who would like college kids and just about everybody
else to be armed to the teeth is that the good guys can shoot back whenever the
bad guys show up to do harm. An important study published in 2009 by researchers
at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine estimated that people in
possession of a gun at the time of an assault were 4.5 times more likely to be
shot during the assault than someone in a comparable situation without a gun.
“On average,” the researchers said, “guns did not seem to protect those who
possessed them from being shot in an assault. Although successful defensive gun
uses can and do occur, the findings of this study do not support the perception
that such successes are likely.”
Approximately 100,000 shootings occur in the United States every year. The
number of people killed by guns should be enough to make our knees go weak.
Monday was a national holiday celebrating the life of the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther
King Jr. While the gun crazies are telling us that ever more Americans need to
be walking around armed, we should keep in mind that more than a million people
have died from gun violence — in murders, accidents and suicides — since Dr.
King was shot to death in 1968.
We need fewer homicides, fewer accidental deaths and fewer suicides. That means
fewer guns. That means stricter licensing and registration, more vigorous
background checks and a ban on assault weapons. Start with that. Don’t tell me
it’s too hard to achieve. Just get started.
How Many Deaths Are
Enough?, NYT, 17.1.2011,
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/01/18/opinion/18herbert.html
Why Not Regulate Guns
as Seriously as Toys?
January 12, 2011
The New York Times
By NICHOLAS D. KRISTOF
Jared Loughner was considered too mentally unstable to attend
community college. He was rejected by the Army. Yet buy a Glock handgun and a
33-round magazine? No problem.
To protect the public, we regulate cars and toys, medicines and mutual funds.
So, simply as a public health matter, shouldn’t we take steps to reduce the toll
from our domestic arms industry?
Look, I’m an Oregon farm boy who was given a .22 rifle for my 12th birthday. I
still shoot occasionally when visiting the family farm, and I understand one
appeal of guns: they’re fun.
It’s also true that city slickers sometimes exaggerate the risk of any one gun.
The authors of Freakonomics noted that a home with a swimming pool is
considerably more dangerous for small children than a home with a gun. They said
that 1 child drowns annually for every 11,000 residential pools, but 1 child is
shot dead for every 1 million-plus guns.
All that said, guns are far more deadly in America, not least because there are
so many of them. There are about 85 guns per 100 people in the United States,
and we are particularly awash in handguns.
(The only country I’ve seen that is more armed than America is Yemen. Near the
town of Sadah, I dropped by a gun market where I was offered grenade launchers,
machine guns, antitank mines, and even an anti-aircraft weapon. Yep, an N.R.A.
dream! No pesky regulators. Just terrorism and a minor civil war.)
Just since the killings in Tucson, another 320 or so Americans have been killed
by guns — anonymously, with barely a whisker of attention. By tomorrow it’ll be
400 deaths. Every day, about 80 people die from guns, and several times as many
are injured.
Handgun sales in Arizona soared by 60 percent on Monday, according to Bloomberg
News, as buyers sought to beat any beefing up of gun laws. People also often buy
guns in hopes of being safer. But the evidence is overwhelming that firearms
actually endanger those who own them. One scholar, John Lott Jr., published a
book suggesting that more guns lead to less crime, but many studies have now
debunked that finding (although it’s also true that a boom in concealed weapons
didn’t lead to the bloodbath that liberals had forecast).
A careful article forthcoming in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine by
David Hemenway, a Harvard professor who wrote a brilliant book a few years ago
reframing the gun debate as a public health challenge, makes clear that a gun in
the home makes you much more likely to be shot — by accident, by suicide or by
homicide.
The chances that a gun will be used to deter a home invasion are unbelievably
remote, and dialing 911 is more effective in reducing injury than brandishing a
weapon, the journal article says. But it adds that American children are 11
times more likely to die in a gun accident than in other developed countries,
because of the prevalence of guns.
Likewise, suicide rates are higher in states with more guns, simply because
there are more gun suicides. Other kinds of suicide rates are no higher. And
because most homicides in the home are by family members or acquaintances — not
by an intruder — the presence of a gun in the home increases the risk of a gun
murder in that home.
So what can be done? I asked Professor Hemenway how he would oversee a public
health approach to reducing gun deaths and injuries. He suggested:
• Limit gun purchases to one per month per person, to reduce gun trafficking.
And just as the government has cracked down on retailers who sell cigarettes to
minors, get tough on gun dealers who sell to traffickers.
• Push for more gun safes, and make serial numbers harder to erase.
• Improve background checks and follow Canada in requiring a 28-day waiting
period to buy a handgun. And ban oversize magazines, such as the 33-bullet
magazine allegedly used in Tucson. If the shooter had had to reload after firing
10 bullets, he might have been tackled earlier. And invest in new technologies
such as “smart guns,” which can be fired only when near a separate wristband or
after a fingerprint scan.
We can also learn from Australia, which in 1996 banned assault weapons and began
buying back 650,000 of them. The impact is controversial and has sometimes been
distorted. But the Journal of Public Health Policy notes that after the ban, the
firearm suicide rate dropped by half in Australia over the next seven years, and
the firearm homicide rate was almost halved.
Congress on Wednesday echoed with speeches honoring those shot in Tucson. That’s
great — but hollow. The best memorial would be to regulate firearms every bit as
seriously as we regulate automobiles or toys.
Why Not Regulate Guns
as Seriously as Toys?, NYT, 12.1.2011,
http://www.nytimes.com/2011/01/13/opinion/13kristof.html
Handguns for 18-Year-Olds?
November 25, 2010
The New York Times
The National Rifle Association keeps coming up with clever new ways to
undermine public safety.
Just in the past year, the gun-rights group sought to scuttle basic gun controls
enacted by the District of Columbia, including a ban on powerful semiautomatic
weapons in the nation’s capital. The group also blocked common-sense efforts in
Congress to bar people on the F.B.I.’s terrorist watch list from buying guns and
explosives. It kept open the deadly loophole in federal law that lets gun
traffickers and other unqualified buyers to obtain weapons without background
checks at gun shows.
Last week, President Obama had barely nominated a new director for the Bureau of
Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives, which is supposed to control firearms
— Andrew Traver, a well-qualified career professional — before the gun lobby
denounced him as “deeply aligned with gun control advocates.” Mr. Traver’s sin?
Associating with a police chief’s group that wants to reduce the use of handguns
on city streets. The nomination was rated dead on arrival in the next Congress,
where the N.R.A. will, if anything, be more powerful.
Finally, the gun lobby has filed two lawsuits in federal court in Lubbock, Tex.,
to compel the State of Texas to allow young people between the ages of 18 and 20
years old to buy handguns and carry them concealed in public places.
The first suit challenges the longstanding federal law prohibiting licensed gun
dealers from selling handguns to anyone under 21 years old. The second case
contests a Texas law setting 21 as the minimum age for carrying a concealed
weapon.
As a legal matter, both lawsuits should fail. In its recent Second Amendment
rulings, the Supreme Court struck down complete bans on handgun ownership, but
explicitly left room for limits on gun ownership and possession by felons and
the mentally ill, and other reasonable restrictions like Texas’ age limitations.
The Supreme Court has said nothing to suggest that the Second Amendment requires
Americans to allow armed teenagers in their communities.
Beyond the dubious legal claims, the idea that young individuals ages 18 to 20
have a constitutional right to buy weapons and carry them loaded and concealed
in public is breathtakingly irresponsible.
Young people in that age range commit a disproportionate amount of gun violence.
F.B.I. crime data from 2009 shows arrests for murder, nonnegligent homicides and
other violent crimes peaking from ages 18 to 20. That age group accounts for
about 5 percent of the population but nearly 20 percent of homicide and
manslaughter arrests, and nearly twice the number of such arrests for those ages
30 to 34, according to the F.B.I. figures.
What the N.R.A. should be doing is keeping our streets and our teenagers safer
by working to extend the prohibition on guns sales to people 18 to 20 years old
by licensed dealers to include unlicensed sellers at gun shows and elsewhere.
Handguns for
18-Year-Olds?, NYT, 25.11.2010,
http://www.nytimes.com/2010/11/26/opinion/26fri1.html
More States Allowing Guns
in Bars and Restaurants
October 3, 2010
The New York Times
By MALCOLM GAY
NASHVILLE — Happy-hour beers were going for $5 at Past Perfect, a cavernous
bar just off this city’s strip of honky-tonks and tourist shops when Adam
Ringenberg walked in with a loaded 9-millimeter pistol in the front pocket of
his gray slacks.
Mr. Ringenberg, a technology consultant, is one of the state’s nearly 300,000
handgun permit holders who have recently seen their rights greatly expanded by a
new law — one of the nation’s first — that allows them to carry loaded firearms
into bars and restaurants that serve alcohol.
“If someone’s sticking a gun in my face, I’m not relying on their charity to
keep me alive,” said Mr. Ringenberg, 30, who said he carries the gun for
personal protection when he is not at work.
Gun rights advocates like Mr. Ringenberg may applaud the new law, but many
customers, waiters and restaurateurs here are dismayed by the decision.
“That’s not cool in my book,” Art Andersen, 44, said as he nursed a Coors Light
at Sam’s Sports Bar and Grill near Vanderbilt University. “It opens the door to
trouble. It’s giving you the right to be Wyatt Earp.”
Tennessee is one of four states, along with Arizona, Georgia and Virginia, that
recently enacted laws explicitly allowing loaded guns in bars. (Eighteen other
states allow weapons in restaurants that serve alcohol.) The new measures in
Tennessee and the three other states come after two landmark Supreme Court
rulings that citizens have an individual right — not just in connection with a
well-regulated militia — to keep a loaded handgun for home defense.
Experts say these laws represent the latest wave in the country’s gun debate, as
the gun lobby seeks, state by state, to expand the realm of guns in everyday
life.
The rulings, which overturned handgun bans in Washington and Chicago, have
strengthened the stance of gun rights advocates nationwide. More than 250
lawsuits now challenge various gun laws, and Gov. Rick Perry of Texas, a
Republican, called for guns to be made legal on campuses after a shooting last
week at the University of Texas, Austin, arguing that armed bystanders might
have stopped the gunman.
The new laws have also brought to light the status of 20 other states — New
York, New Jersey and Massachusetts among them — that do not address the
question, appearing by default to allow those with permits to carry guns into
establishments that serve alcohol, according to the Legal Community Against
Violence, a nonprofit group that promotes gun control and tracks state gun laws.
“A lot of states for a long time have not felt the need to say you could or
couldn’t do it,” said Paul Helmke, president of the Brady Campaign to Prevent
Gun Violence. “There weren’t as many conceal-carry permits out there, so it
wasn’t really an issue.” Now, he said, “the attitude from the gun lobby is that
they should be able to take their guns wherever they want. In the last year,
they’re starting to move toward needing no permit at all.”
State Representative Curry Todd, a Republican who first introduced the
guns-in-bars bill here, said that carrying a gun inside a tavern was never the
law’s primary intention. Rather, he said, the law lets people defend themselves
while walking to and from restaurants.
“Folks were being robbed, assaulted — it was becoming an issue of personal
safety,” said Mr. Todd, who added that the National Rifle Association had aided
his legislative efforts. “The police aren’t going to be able to protect you.
They’re going to be checking out the crime scene after you and your family’s
been shot or injured or assaulted or raped.”
Under Tennessee’s new law, gun permit holders are not supposed to drink alcohol
while carrying their weapons. Mr. Ringenberg washed down his steak sandwich with
a Coke.
But critics of the law say the provision is no guarantee of safety, pointing to
a recent shooting in Virginia where a customer who had a permit to carry a
concealed weapon shot himself in the leg while drinking beer at a restaurant.
“Guns and alcohol don’t mix; that’s the bottom line,” said Michael Drescher, a
spokesman for Governor Phil Bredesen of Tennessee, a Democrat, who vetoed the
bill but was overridden by the legislature.
The law allows restaurant and bar owners to prohibit people from carrying
weapons inside their establishments by posting signs out front. But many
restaurateurs are reluctant to discourage the patronage of gun owners, often
saying privately that they do not allow guns but holding off on posting a sign.
“I’ve talked to a lot of restaurants, and probably 50 to 60 percent of them have
no clue what’s going on,” said Ray Friedman, 51, who has created a Web site
listing the firearms policies of area restaurants.
Previously, states like Tennessee did not allow its residents to carry concealed
weapons unless they had a special permit from the local authorities. That began
to shift in the mid-1990s, as the gun lobby pushed states to adopt policies that
made permits for concealed weapons more accessible.
The new law passed with broad legislative support, despite opposition from the
Nashville Chamber of Commerce and the Tennessee Hospitality Association.
So far, the law has been challenged only once. Filed by an anonymous waiter, the
complaint contended that allowing guns into a tavern creates an unsafe work
environment for servers. His complaint was denied by the state’s Division of
Occupational Safety and Health.
“A loaded concealed weapon in a bar is a recognized hazard,” said David Randolph
Smith, a lawyer who represents the waiter and is preparing to appeal the
decision. “I have a right to go into a restaurant or bar and not have people
armed. And of course, the waiter has a right to a safe workplace.”
Down at Bobby’s Idle Hour, however, Mike Gideon said he did not believe that
guns in bars were unsafe. As he sipped a beer in the fading afternoon light, Mr.
Gideon, who characterized his 19-gun collection as “serious,” said that having a
few permit holders around made any public space safer and that he boycotts any
business that does not allow him to carry a weapon.
“People who have gun permits have the cleanest records around,” said Mr. Gideon,
54. “The guy that’s going to do the bad thing? He’s not worried about the law at
all. The ‘No Guns’ sign just says to him, ‘Hey, buddy, smooth sailing.’ ”
More States Allowing
Guns in Bars and Restaurants, NYT, 3.11.2010,
http://www.nytimes.com/2010/10/04/us/04guns.html
The Court:
Ignoring the Reality of Guns
June 28, 2010
The New York Times
About 10,000 Americans died by handgun violence, according to federal
statistics, in the four months that the Supreme Court debated which clause of
the Constitution it would use to subvert Chicago’s entirely sensible ban on
handgun ownership. The arguments that led to Monday’s decision undermining
Chicago’s law were infuriatingly abstract, but the results will be all too real
and bloody.
This began two years ago, when the Supreme Court disregarded the plain words of
the Second Amendment and overturned the District of Columbia’s handgun ban,
deciding that the amendment gave individuals in the district, not just militias,
the right to bear arms. Proceeding from that flawed logic, the court has now
said the amendment applies to all states and cities, rendering Chicago’s ban on
handgun ownership unenforceable.
Once again, the court’s conservative majority imposed its selective reading of
American history, citing the country’s violent separation from Britain and the
battles over slavery as proof that the authors of the Constitution and its later
amendments considered gun ownership a fundamental right. The court’s members
ignored the present-day reality of Chicago, where 258 public school students
were shot last school year — 32 fatally.
Rather than acknowledging Chicago’s — and the nation’s — need to end an epidemic
of gun violence, the justices spent scores of pages in the decision analyzing
which legal theory should bind the Second Amendment to the states. Should it be
the due process clause of the 14th Amendment, or the amendment’s immunities
clause? The argument was not completely settled because there was not a
five-vote majority for either path.
The issue is not trivial; had the court backed the immunity-clause path
championed by Justice Clarence Thomas, it might have had the beneficial effect
of applying more aspects of the Bill of Rights to the states. That could make it
easier to require that states, like the federal government, have unanimous jury
verdicts in criminal trials, for example, or ban excessive fines.
While the court has now twice attacked complete bans on handgun ownership, the
decision left plenty of room for restrictions on who can buy and sell arms.
The court acknowledged, as it did in the District of Columbia case, that the
amendment did not confer “a right to keep and carry any weapon whatsoever in any
manner whatsoever and for whatever purpose.” It cited a few examples of what it
considered acceptable: limits on gun ownership by felons or the mentally ill,
bans on carrying firearms in sensitive places like schools or government
buildings and conditions on gun sales.
Mayors and state lawmakers will have to use all of that room and keep adopting
the most restrictive possible gun laws — to protect the lives of Americans and
aid the work of law enforcement officials. They should continue to impose
background checks, limit bulk gun purchases, regulate dealers, close gun-show
loopholes.
They should not be intimidated by the theoretical debate that has now concluded
at the court or the relentless stream of lawsuits sure to follow from the gun
lobby that will undoubtedly keep pressing to overturn any and all restrictions.
Officials will have to press back even harder. Too many lives are at stake.
The Court: Ignoring the
Reality of Guns, NYT, 28.6.2010,
http://www.nytimes.com/2010/06/29/opinion/29tue1.html
Justices Say
Gun Rights Apply Locally
The New York Times
June 28, 2010
By THE ASSOCIATED PRESS
WASHINGTON (AP) -- The Supreme Court held Monday that the
Constitution's Second Amendment restrains government's ability to significantly
limit "the right to keep and bear arms," advancing a recent trend by the John
Roberts-led bench to embrace gun rights.
By a narrow, 5-4 vote, the justices signaled, however, that less severe
restrictions could survive legal challenges.
Writing for the court in a case involving restrictive laws in Chicago and one of
its suburbs, Justice Samuel Alito said that the Second Amendment right "applies
equally to the federal government and the states."
The court was split along familiar ideological lines, with five
conservative-moderate justices in favor of gun rights and four liberals opposed.
Chief Justice Roberts voted with the majority.
Two years ago, the court declared that the Second Amendment protects an
individual's right to possess guns, at least for purposes of self-defense in the
home.
That ruling applied only to federal laws. It struck down a ban on handguns and a
trigger lock requirement for other guns in the District of Columbia, a federal
city with a unique legal standing. At the same time, the court was careful not
to cast doubt on other regulations of firearms here.
Gun rights proponents almost immediately filed a federal lawsuit challenging gun
control laws in Chicago and its suburb of Oak Park, Ill, where handguns have
been banned for nearly 30 years. The Brady Center to Prevent Gun Violence says
those laws appear to be the last two remaining outright bans.
Lower federal courts upheld the two laws, noting that judges on those benches
were bound by Supreme Court precedent and that it would be up to the high court
justices to ultimately rule on the true reach of the Second Amendment.
The Supreme Court already has said that most of the guarantees in the Bill of
Rights serve as a check on state and local, as well as federal, laws.
Monday's decision did not explicitly strike down the Chicago area laws, ordering
a federal appeals court to reconsider its ruling. But it left little doubt that
they would eventually fall.
Still, Alito noted that the declaration that the Second Amendment is fully
binding on states and cities "limits (but by no means eliminates) their ability
to devise solutions to social problems that suit local needs and values."
Justices Say Gun Rights
Apply Locally, NYT, 28.6.2010,
http://www.nytimes.com/aponline/2010/06/28/us/AP-US-SupremeCourt-Guns.html
Pastor Urges His Flock
to Bring Guns to Church
June 26, 2009
The New York Times
By KATHARINE Q. SEELYE
LOUISVILLE, Ky. — Ken Pagano, the pastor of the New Bethel Church here, is
passionate about gun rights. He shoots regularly at the local firing range, and
his sermon two weeks ago was on “God, Guns, Gospel and Geometry.” And on
Saturday night, he is inviting his congregation of 150 and others to wear or
carry their firearms into the sanctuary to “celebrate our rights as Americans!”
as a promotional flier for the “open carry celebration” puts it.
“God and guns were part of the foundation of this country,” Mr. Pagano, 49, said
Wednesday in the small brick Assembly of God church, where a large wooden cross
hung over the altar and two American flags jutted from side walls. “I don’t see
any contradiction in this. Not every Christian denomination is pacifist.”
The bring-your-gun-to-church day, which will include a $1 raffle of a handgun,
firearms safety lessons and a picnic, is another sign that the gun culture in
the United States is thriving despite, or perhaps because of, President Obama’s
election in November.
Last year, the National Rifle Association ran a multimillion-dollar advertising
campaign against Mr. Obama, stoking fears that he would be the most antigun
president in history and that firearms would be confiscated. One worry was that
a Democratic president and Congress would reinstitute the assault-weapons ban,
which expired in 2004.
But there is little support for the ban. Mr. Obama and his party have largely
ignored gun-control issues, and the president even signed a measure that will
allow firearms in national parks.
Still, the fear remains that Mr. Obama, and his attorney general, Eric H. Holder
Jr., will crack down on guns sooner or later. That — along with the faltering
economy, which gun sellers say has spurred purchases for self-defense — has
fueled a record surge in gun sales.
“Every president wants to be re-elected, and gun bans are pretty much a
nonstarter for getting re-elected,” said Win Underwood, owner of the Bluegrass
Indoor Range here. “What I suspect is going to happen is, Obama’s going to cool
his jets until he can get re-elected, and then he’ll start building his legacy
in these hot-button areas.”
When Mr. Obama was elected in November, federal instant background checks, the
best indicator of gun sales, jumped 42 percent over the previous November. Every
month since then, the number of checks has been higher than the year before,
although the postelection surge may be tapering off, as all surges eventually
do. While the number of checks in April increased 30 percent from the year
before, the number of checks in May (1,023,102) was only 15 percent higher than
in May 2008.
The National Rifle Association says its membership is up 30 percent since
November. And several states have recently passed laws allowing gun owners to
carry firearms in more places — bars, restaurants, cars and parks.
“We have a very active agenda in all 50 states,” said Chris W. Cox, legislative
director of the N.R.A., widely considered the country’s most powerful lobby. “We
have right-to-carry laws in over 40 states; 20 years ago, it was in just six.”
Of the 40 states with right-to-carry laws, 20 allow guns in churches.
Public attitudes also seem to be turning more sympathetic to gun owners. In
April, the Pew Research Center found for the first time that almost as many
people said it was more important to protect the rights of gun owners (45
percent) than to control gun ownership (49 percent). Just a year ago, Pew said,
58 percent said gun control was more important than the rights of gun owners (37
percent).
Gun-control advocates say they feel increasingly ineffective, especially after a
recent spate of high-profile shootings, including last month’s murder, inside a
church in Kansas, of a doctor who performed late-term abortions.
“We’ve definitely been marginalized,” said Pam Gersh, a public relations
consultant here who helped organize a rally in Louisville in 2000, to coincide
with the Million Mom March against guns in Washington.
“The Brady Campaign and other similar organizations who advocate sensible gun
responsibility laws don’t have the money and the political power — not even
close,” she said. “This pastor is obviously crossing a line here and saying ‘I
can even take my guns to church, and there is nothing you can do about it.’ ”
Ms. Gersh said she was not aware that a group of local churches and peace
activists were staging a counterpicnic — called “Bring your peaceful heart,
leave your gun at home” — at the same time as Mr. Pagano’s event.
But news media attention — some from overseas — has focused on Mr. Pagano, who
has been planning the event for a year, in celebration of the Fourth of July.
Cameras will not be allowed in the church, he said, to protect the
congregation’s privacy.
The celebration will feature lessons in responsible gun ownership, Mr. Pagano
said. Sheriff’s deputies will be at the doors to check that openly carried
firearms are unloaded, but they will not check for concealed weapons.
“That’s the whole point of concealed,” Mr. Pagano said, adding that he was not
worried because such owners require training.
Mr. Pagano said the church’s insurance company, which he would not identify, had
canceled the church’s policy for the day on Saturday and told him that it would
cancel the policy for good at the end of the year. If he cannot find insurance
for Saturday, people will not be allowed in openly carrying their guns.
Arkansas and Georgia recently rejected efforts to allow people to carry
concealed weapons in church. Watching the debate in Arkansas was John Phillips,
pastor of the Central Church of Christ in Little Rock. In 1986, Mr. Phillips was
preaching in a different church there when a gunman shot him and a parishioner.
Both survived, but Mr. Phillips, 51, still has a bullet lodged in his spine.
In a telephone interview, he said he found the idea of “packing in the pew”
abhorrent.
“There is a movement afoot across the nation, with the gun lobby pushing the
envelope, trying to allow concealed weapons to be carried in places where they
used to be prohibited — churches, schools, bars,” Mr. Phillips said.
“I don’t understand how any minister who is familiar with the teachings of the
Bible can do this,” he added. “Jesus didn’t say, ‘Go ahead, make my day.’ ”
Mr. Pagano takes such comments as a challenge to his faith and says they make
him more determined.
“When someone from within the church tells me that being a Christian and having
firearms are contradictions, that they’re incompatible with the Gospel —
baloney,” he said. “As soon as you start saying that it’s not something that
Christians do, well, guns are just the foil. The issue now is the Gospel. So in
a sense, it does become a crusade. Now the Gospel is at stake.”
Pastor Urges His Flock
to Bring Guns to Church, NYT, 26.6.2009,
http://www.nytimes.com/2009/06/26/us/26guns.html
Gun Rulings Open Way
to Supreme Court Review
June 17, 2009
The New York Times
By JOHN SCHWARTZ
A year ago, the United States Supreme Court issued a landmark decision
establishing the constitutional right of Americans to own guns. But the justices
did not explain what the practical effect of that ruling would be on city and
state gun laws.
Could a city still ban handguns? The justices said the District of Columbia
could not, but only because it is a special federal district. The question of
the constitutionality of existing city and state gun laws was left unanswered.
That left a large vacuum for the lower courts to fill. Supporters of gun rights
filed a flurry of lawsuits to strike down local gun restrictions, and now
federal appeals courts have begun weighing in on this divisive issue, using very
different reasoning.
One court this month upheld Chicago’s ban on automatic weapons and concealed
handguns, while in April a California court disagreed on the constitutional
issue.
The differing opinions mean that the whole issue of city and state gun laws will
probably head back to the Supreme Court for clarification, leading many legal
experts to predict a further expansion of gun rights.
The new cases are fallout from last year’s Supreme Court case, District of
Columbia v. Heller, which struck down parts of Washington’s gun control
ordinance, the strictest in the country, and stated for the first time that the
Second Amendment gives individuals a right to keep and bear arms for personal
use. But the court declined to say whether the Second Amendment in general
applies to state and local governments.
In January, the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit, in New
York, in a ruling joined by Judge Sonia Sotomayor, declined to apply the Second
Amendment to a New York law that banned the martial arts device known as chukka
sticks. The ban was allowed to stay in place.
Then in April, a three-judge panel of the Ninth Circuit, in San Francisco, ruled
that the Second Amendment did apply to the states, even though it allowed a
California county to ban guns on government property like state fairgrounds.
That case, Nordyke v. King, is being considered for a rehearing by the full
Ninth Circuit.
Those two conflicting cases set the stage for two other cases that were heard as
one in the Seventh Circuit in Chicago, testing that city’s handgun ban. On June
2, a three-judge panel of the court, led by Chief Judge Frank H. Easterbrook, a
well-known conservative, ruled that there was no basis for the court to apply
the Second Amendment to the states. Such a decision, Judge Easterbrook wrote,
should be made only by the Supreme Court, not at the appellate level.
The right of states to make their own decisions on such matters, Judge
Easterbrook wrote, “is an older and more deeply rooted tradition than is a right
to carry any particular kind of weapon.”
The lawyers for the plaintiffs, including the National Rifle Association, have
asked the Supreme Court to take up the Chicago cases.
A split among the federal appeals circuits, especially on constitutional issues,
invites Supreme Court action, said Adam Winkler, a law professor at the
University of California, Los Angeles.
“Californians, Hawaiians and Oregonians have a Second Amendment right to bear
arms, but New Yorkers, Illinoisans, and Wisconsinites don’t,” Professor Winkler
said. “The Supreme Court will want to correct this sooner rather than later.”
The process of applying amendments of the Bill of Rights to the states, known as
incorporation, began after the Civil War but had its heyday in the activist
Supreme Court of the Earl Warren era. Much of the Bill of Rights, including the
First Amendment’s freedom of speech and some rights of criminal defendants, have
been applied to the states, but other elements have not, including the Seventh
Amendment right to a civil jury trial and the Second Amendment.
Incorporation fell out of favor after the 1960s, but a new generation of largely
liberal scholars of law and history have brought it back into the intellectual
mainstream, said Akhil Reed Amar, a law professor at Yale University, who
supports the process.
“The precedents are now supportive of incorporation of nearly every provision of
the Bill of Rights,” Professor Amar said. “Now what’s odd is that the Second
Amendment doesn’t apply to the states.”
Sanford Levinson, a law professor at the University of Texas, said he would be
surprised if the Supreme Court accepted these gun cases, because some of the
conservative justices on the court had scoffed at incorporation arguments in the
past and might not want to set a precedent.
Professor Amar, however, argued that the justices would not only take up the
case but would also ultimately vote for incorporation of the Second Amendment.
Even if the Second Amendment becomes the controlling law of every state and
town, constitutional scholars say it is still unlikely that gun laws would be
overturned wholesale. The Supreme Court’s Heller decision last year, notes
Nelson Lund, a law professor at George Mason University, “clearly indicates that
governments will still have wide latitude to regulate firearms.”
Even the Ninth Circuit in California, while applying the Second Amendment to the
states, still upheld the gun ordinance that gave rise to the lawsuit.
Eugene Volokh, a law professor at the University of California, Los Angeles,
said the view of the Ninth Circuit reflected what polls have said was, by and
large, the view of the American people.
“There is a right to bear arms,” Professor Volokh said, “but it’s not absolute.”
Gun Rulings Open Way to
Supreme Court Review, NYT, 17.6.2009,
http://www.nytimes.com/2009/06/17/us/17guns.html
In Texas School,
Teachers Carry Books and Guns
August 29, 2008
The New York Times
By JAMES C. McKINLEY Jr.
HARROLD, Tex. — Students in this tiny town of grain silos and ranch-style
houses spent much of the first couple of days in school this week trying to
guess which of their teachers were carrying pistols under their clothes.
“We made fun of them,” said Eric Howard, a 16-year-old high school junior.
“Everybody knows everybody here. We will find out.”
The school board in this impoverished rural hamlet in North Texas has drawn
national attention with its decision to let some teachers carry concealed
weapons, a track no other school in the country has followed. The idea is to
ward off a massacre along the lines of what happened at Columbine High School in
Colorado in 1999.
“Our people just don’t want their children to be fish in a bowl,” said David
Thweatt, the schools superintendent and driving force behind the policy.
“Country people are take-care-of-yourself people. They are not under the
illusion that the police are there to protect them.”
Even in Texas, with its tradition of lenient gun laws and frontier justice, the
idea of teachers’ taking guns to class has rattled some people and sparked a
fiery debate.
Gun-control advocates are wringing their hands, while pro-gun groups are
gleeful. Leaders of the state’s major teachers unions have expressed stunned
outrage, while the conservative Republican governor, Rick Perry, has endorsed
the idea.
In the center of the storm is Mr. Thweatt, a man who describes himself as “a
contingency planner,” who believes Americans should be less afraid of protecting
themselves and who thinks signs at schools saying “gun-free zone” make them
targets for armed attacks. “That’s like saying sic ’em to a dog,” he said.
Mr. Thweatt maintains that having teachers carry guns is a rational response to
a real threat. The county sheriff’s office is 17 miles away, he argues, and the
district cannot afford to hire police officers, as urban schools in Dallas and
Houston do.
The school board decided that teachers with concealed guns were a better form of
security than armed peace officers, since an attacker would not know whom to
shoot first, Mr. Thweatt said. Teachers have received training from a private
security consultant and will use special ammunition designed to prevent
ricocheting, he added.
Harrold, about 180 miles northwest of Dallas, is a far cry from the giant
districts in major Texas cities, where gang violence is the main concern and
most schools have their own police forces. Barely 100 students of all ages
attend classes here in two brick buildings built more than 60 years ago. There
are two dozen teachers, a handful of buses and a football field bordered by
crops.
Yet the town is not isolated in rustic peace, supporters of the plan point out.
A four-lane highway runs through town, bringing with it a river of humanity,
including criminals, they say. The police recently shut down a drug-producing
laboratory in a ramshackle house near school property. Drifters sometimes sleep
under the overpass.
“I’m not exactly paranoid,” Mr. Thweatt said. “I like to consider myself
prepared.”
Some residents and parents, however, think Mr. Thweatt may be overstating the
threat. Many say they rarely lock their doors, much less worry about random
drifters with pistols running amok at the school. Longtime residents were
hard-pressed to recall a single violent incident there.
Others worry that introducing guns into the classroom might create more problems
than it solved. A teacher tussling with a student could lose control of a
weapon, or a gun might go off by accident, they said.
“I don’t think there is a place in the school whatsoever for a gun unless you
have a police officer in there,” said Bobby G. Brown, a farmer and former school
board chairman whose two sons were educated at the school. “I don’t care how
much training they have.”
His wife, Diane Brown, added: “There are too many things that could happen. They
are not trained to make life-and-death-situation judgments.”
Mr. Thweatt declined to say how many teachers were armed, or who they were, on
the theory that it would tip off the bad guys. He also declined to identify the
private consultant who provided teachers with about 40 hours of weapons
training.
Most critics question whether teachers, even with extra training, are as
qualified as police officers to take out an armed attacker.
“We are trained to teach and to educate,” said Zeph Capo, the legislative
director for the Houston Association of Teachers. “We are not trained to tame
the Wild West.”
Texas gun laws ban the weapons on school property. But the Legislature carved
out an exception allowing school boards to permit people with concealed handgun
licenses to carry their weapons. No local district had taken advantage of the
exception until the Harrold school board acted.
Debbie Ratcliffe, a spokeswoman for the Texas Education Agency, said the state’s
hands were tied. “We have really tried not to get involved in this,” Ms.
Ratcliffe said. “Frankly, it’s a matter of local control.”
Gun-control advocates say, however, that while the school district may be
complying with state gun laws, it appears to be violating the education statute.
That law says “security personnel” authorized to carry weapons on campuses must
be “commissioned peace officers,” who undergo police training.
“It seems to us not only an unwise policy but an illegal one,” said Brian
Siebel, a lawyer in Washington for the Brady Campaign to Prevent Gun Violence.
The school district has countered that teachers are not “security personnel” and
so do not need to become peace officers.
As a general rule, the seven school board members — a collection of farmers and
oil workers led by an ambulance medic — have referred all questions from
reporters to Mr. Thweatt. But one member, Coy Cato, gave a short interview. “In
my opinion, it is the best way to protect our kids,” Mr. Cato said. Asked if
others in the community shared his view, he said that he had not taken a poll,
but “I think so.”
Still, several residents complained that the board made little or no effort to
gather public opinion on the matter. Some said they did not hear about the plan
until reporters started asking questions about it in early August.
Mr. Thweatt said the board discussed the proposal for nearly two years and
considered several options — tranquilizer guns, beanbag guns, Tasers, Mace and
armed security guards — but each was found lacking in some way. “We
devil-advocated it to death,” Mr. Thweatt said.
That discussion went unnoticed by many parents.
Traci McKay, a 34-year-old restaurant employee, sends three children to the
school, yet said she had not heard about the pistol-carrying teachers until two
weeks before the start of the semester. She was stunned.
“I should have been informed,” Ms. McKay said. “If something happens, do we
really want all these people shooting at each other?”
Ms. McKay said Mr. Thweatt had yet to explain why a town with such a low crime
rate needed such measures. She is afraid, however, that her children might face
repercussions if she takes up a petition against the idea.
“We are pretty much being told to deal with this or move,” Ms. McKay said.
In Texas School,
Teachers Carry Books and Guns,
NYT,
29.8.2008,
http://www.nytimes.com/2008/08/29/us/29texas.html
Justices
Rule
for Individual Gun Rights
June 27,
2008
The New York Times
By DAVID STOUT
WASHINGTON
— The Supreme Court declared for the first time on Thursday that the
Constitution protects an individual’s right to have a gun, not just the right of
the states to maintain militias.
Justice Antonin Scalia, writing for the majority in the landmark 5-to-4
decision, said the Constitution does not allow “the absolute prohibition of
handguns held and used for self-defense in the home.” In so declaring, the
majority found that a gun-control law in the nation’s capital went too far by
making it nearly impossible to own a handgun.
But the court held that the individual right to possess a gun “for traditionally
lawful purposes, such as self-defense within the home” is not unlimited. “It is
not a right to keep and carry any weapon whatsoever in any manner whatsoever and
for whatever purpose,” Justice Scalia wrote.
The ruling does not mean, for instance, that laws against carrying concealed
weapons are to be swept aside. Furthermore, Justice Scalia wrote, “The court’s
opinion should not be taken to cast doubt on longstanding prohibitions on the
possession of firearms by felons and the mentally ill, or laws forbidding the
carrying of firearms in sensitive places such as schools and government
buildings, or laws imposing conditions and qualifications on the commercial sale
of arms.”
The decision upheld a federal appeals court ruling that the District of
Columbia’s gun law, one of the strictest in the country, went beyond
constitutional limits. Not only did the 1976 law make it practically impossible
for an individual to legally possess a handgun in the district, but it also
spelled out rules for the storage of rifles and shotguns. But the court did not
articulate a specific standard of review for what might be a reasonable
restraint on the right to possess a firearm.
The court also said on Thursday that the district law’s requirement that lawful
weapons be rendered essentially inoperable, by trigger locks or disassembly, was
unconstitutional because it rendered the weapons useless for self-defense.
Joining Justice Scalia were Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr. and Justices
Clarence Thomas, Anthony M. Kennedy and Samuel A. Alito Jr.
A dissent by Justice John Paul Stevens asserted that the majority “would have us
believe that over 200 years ago, the framers made a choice to limit the tools
available to elected officials wishing to regulate civilian uses of weapons.”
Joining him were Justices David H. Souter, Ruth Bader Ginsburg and Stephen G.
Breyer.
The high court’s ruling was the first since 1939 to deal with the scope of the
Second Amendment, and the first to so directly address the meaning of the
amendment’s ambiguous, comma-laden text: “A well regulated Militia, being
necessary to the security of a free State, the right of the people to keep and
bear Arms, shall not be infringed.”
Not surprisingly, Justice Scalia and Justice Stevens differed on the clarity (or
lack thereof) of the Second Amendment. “The amendment’s prefatory clause
announces a purpose, but does not limit or expand the scope of the second
clause,” wrote Justice Scalia. “The operative clause’s text and history
demonstrate that it connotes an individual right to keep and bear arms.”
Not at all, Justice Stevens countered, asserting that the majority “stakes its
holding on a strained and unpersuasive reading of the amendment’s text.” Justice
Stevens read his dissent from the bench, an unmistakable signal that he
disagreed deeply with the majority.
Indeed, it was clear from the conflicting opinions of Justices Scalia and
Stevens that the case had generated emotional as well as intellectual sparks at
the court.
Justice Scalia devoted page after page of his opinion to the various state
constitutions and to the use of language in the 18th and 19th centuries to
support his view that an individual right to bear arms is embodied in the
Constitution. And Justice Scalia, who clearly takes pride in his writing as well
as his reasoning, used adjectives like “frivolous” and “bizarre” to describe the
other side’s arguments.
Not to be outdone, Justice Stevens called the majority’s interpretation of the
Second Amendment “overwrought and novel” and said it “calls to mind the parable
of the six blind men and the elephant,” in which each of the sightless men had a
different conception of the animal.
“Each of them, of course, has fundamentally failed to grasp the nature of the
creature,” Justice Stevens wrote.
The ruling on Thursday will surely not quiet the debate about guns and violence
in the United States, where deaths by firearm take a far higher toll than in
many other countries, as Justice Scalia acknowledged.
“We are aware of the problem of handgun violence in this country,” he wrote,
saying that he took seriously the concerns of those who believe that
“prohibition of handgun ownership is a solution.”
Lawmakers in the District of Columbia and across the country may look to the
decision as a blueprint for writing new legislation to satisfy the demands of
constituents who say there is too much regulation of firearms now, or too
little, depending on the sentiments in their regions. (Washington’s Mayor,
Adrian M. Fenty, will instruct the police department to issue new
handgun-registration rules within 30 days while city officials study the ruling,
The Washington Post reported on its Web site.)
Nor was there any suggestion that the court’s ruling would lead to a
proliferation of deadly, military-style assault weapons. Alluding to the 1939
Supreme Court decision, which held that the weapons protected under the Second
Amendment were those “in common use at the time,” Justice Scalia said, “We think
that limitation is fairly supported by the historical tradition of prohibiting
the carrying of ‘dangerous and unusual weapons.’ ”
The White House issued a statement saying that President Bush “strongly agrees
with the Supreme Court’s historic decision today that the Second Amendment
protects the individual right of Americans to keep and bear arms.”
The Supreme Court ruling is likely to play out in this year’s elections, as
Senator John McCain of Arizona, the presumptive Republican nominee for
president, made clear. “I applaud this decision as well as the overturning of
the District of Columbia’s ban on handguns and limitations on the ability to use
firearms for self-defense,” Mr. McCain said in a statement, which contained a
reminder that his Democratic nominee, Senator Barack Obama of Illinois, refused
to join him in signing an amicus brief in support of overturning the district’s
law.
Indeed, Mr. Obama’s view, expressed in a statement, was more nuanced than Mr.
McCain’s. “I have always believed that the Second Amendment protects the right
of individuals to bear arms, but I also identify with the need for crime-ravaged
communities to save their children from the violence that plagues our streets
through common-sense, effective safety measures,” Mr. Obama said, predicting
that the ruling would provide needed guidance for lawmakers.
The National Rifle Association and other supporters of rights to have firearms
are sure to use the decision as a launch pad for lawsuits. The N.R.A. said it
would file suits in San Francisco, Chicago and several Chicago suburbs
challenging handgun restrictions there. “I consider this the opening salvo in a
step-by-step process of providing relief for law-abiding Americans everywhere
that have been deprived of this freedom,” Wayne LaPierre, executive vice
president of the N.R.A., told The Associated Press.
Reaction on Capitol Hill differed sharply. Representative John A. Boehner of
Ohio, the Republican minority leader in the House, applauded the ruling. “The
Constitution plainly guarantees the solemn right to keep and bear arms, and the
whims of politically correct bureaucrats cannot take it away,” he said in a
statement.
But Senator Dianne Feinstein, Democrat of California and a former mayor of San
Francisco, said she was disappointed in the ruling. “I speak as a former mayor,”
she said at a session of the Senate Judiciary Committee. “I speak as somebody
who has gone to homicide crime scenes.”
The last time the Supreme Court weighed a case involving the Second Amendment,
in 1939, it decided a narrower question, finding that the Constitution did not
protect any right to possess a specific type of firearm, the sawed-off shotgun.
By contrast, the issues in the District of Columbia case seemed much more
“mainstream,” if that term can be used in reference to gun-control issues. When
the justices announced on Nov. 20 that they were accepting the case of District
of Columbia v. Heller, No. 07-290, they indicated that they would go to the
heart of the long debate.
The question, they said, is whether the district’s restrictions on firearms
“violate the Second Amendment rights of individuals who are not affiliated with
any state-regulated militia but who wish to keep handguns and other firearms for
private use in their homes.”
Dick Anthony Heller, a security guard who carries a handgun for his job
protecting federal judiciary offices, challenged the District of Columbia’s law
after his request for a license to keep his gun at home was rejected.
There have been debates about the efficacy of gun-control efforts in the
capital. Those district residents who want guns — and are willing to risk
punishment if caught with them without bothering to apply for permits — can get
them easily enough, across the Potomac River in Virginia and in other nearby
states.
Washington’s homicide rate, while high by world standards, is sharply lower than
it was in the early 1990s. Last year, there were 181 homicides in Washington,
down from a peak of 479 in 1991, when crack cocaine was a huge problem in some
sections of the city.
Concluding his opinion, Justice Scalia wrote, “Undoubtedly some think that the
Second Amendment is outmoded in a society where our standing army is the pride
of our nation, where well-trained police forces provide personal security, and
where gun violence is a serious problem.”
“That is perhaps debatable,” Justice Scalia wrote, “but what is not debatable is
that it is not the role of this court to pronounce the Second Amendment
extinct.”
When the Heller case was argued before the justices on March 18, Mr. Heller’s
lawyer, Alan Gura, did not assert that the Second Amendment precluded any kind
of ban related to gun possession. He said that a ban on the shipment of machine
guns and sawed-off shotguns would be acceptable, and in answer to a question
from the justices, so, too, might be a prohibition on guns in schools. Some of
the justices signaled during arguments that they thought the District’s
near-total ban on handguns went too far.
A legislature “has a great deal of leeway in regulating firearms,” Mr. Gura
argued, but not to the extent of virtually banning them in homes.
The Washington law not only established high barriers to the private possession
of handguns, it also required that rifles and shotguns be kept either in a
disassembled state or under a trigger lock.
Walter Dellinger, the lawyer who argued for the district on March 18, asserted
that “the people” and “the militia” were essentially the same, and that the
Second Amendment gave people the right to bear arms only in connection with
their militia service.
Solicitor General Paul D. Clement, representing the federal government, argued
on behalf of the individual-rights position, which has been the Bush
administration’s policy. But he said that the appeals court had also gone too
far in overturning the ordinance and that the right to bear arms was always
subject to “reasonable regulations.”
Justices Rule for Individual Gun Rights,
NYT,
27.6.2008,
https://www.nytimes.com/2008/06/27/
washington/27scotuscnd.html
Related > Anglonautes >
Vocapedia
gun violence > USA
gun violence > police shootings > USA
violence, abuse, prostitution,
sexual violence, rape, harassment,
kidnapping, crime, police,
arrest, investigation, custody,
police misconduct / brutality / violence > USA
drugs > Mexico, UK, USA
www >
cyberbullying, online abuse / violence
USA >
U.S. Constitution > Second Amendment
Related > Anglonautes > Videos > Documentaries > USA
2020s > Gun
culture, gun violence, gun control
2010s > Gun culture, gun violence, gun control
Related > Anglonautes > History >
17th-20th
century > America, USA
20th century >
USA > Civil rights
17th, 18th, 19th, 20th century
English America, America, USA
Racism, Slavery,
Abolition, Civil war,
Abraham Lincoln,
Reconstruction
17th, 18th, 19th century
English America, America, USA
|